On-page SEO, or on-site SEO, refers to optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. This involves optimizing the content and HTML source code of a page, unlike off-page SEO, which affects external signals such as backlinks.
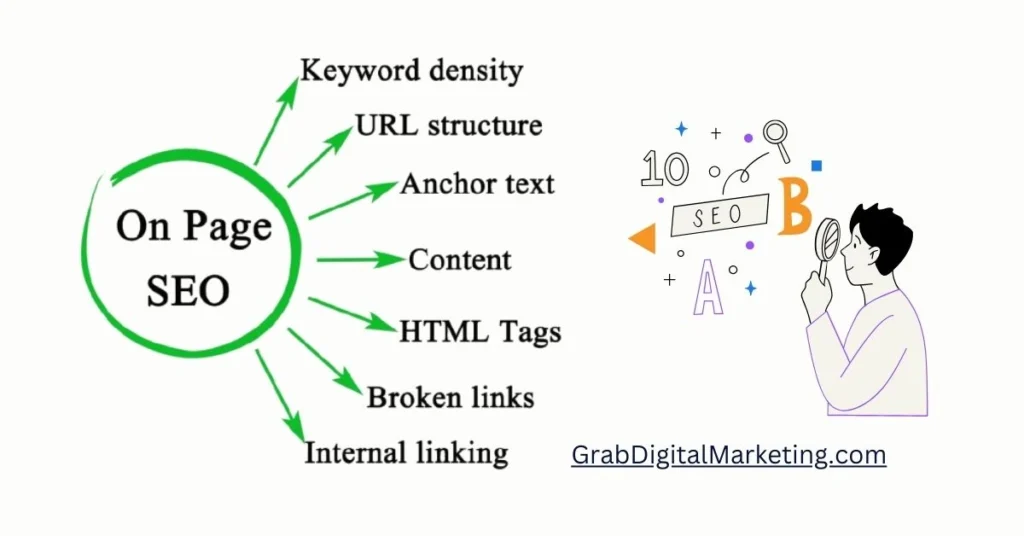
Table of Contents
1. Content Quality

Content is the heart of on-page SEO. High-quality content satisfies user intent, provides valuable information, and engages readers. Some key aspects of content quality include:
- Relevance: Ensure your content is relevant to the target audience and covers the topic comprehensively.
- Originality: Avoid duplicate content. Use unique insights, data, and perspectives.
- Depth: In-depth articles that thoroughly explore a topic tend to perform better.
- Multimedia: Incorporate images, videos, infographics, and other media to enhance the user experience.
2. Keyword Optimization

Effective keyword usage is vital for on-page SEO. This includes:
- Keyword Research: Identify keywords and phrases that potential customers are searching for.
- Keyword Placement: Use primary and secondary keywords in the title, headings, meta descriptions, and throughout the content.
- Keyword Density: Avoid keyword stuffing. Ensure keywords appear naturally and contextually.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Include long-tail keywords that are specific and less competitive.
3. Meta Tags

Meta tags provide search engines with information about your page. Important meta tags include:
- Title Tag: A crucial ranking factor, the title tag should be concise, descriptive, and include the primary keyword.
- Meta Description: A summary of the page content, the meta description should be compelling and include relevant keywords.
- Header Tags: Use H1, H2, H3, etc., to structure content and highlight important sections.
4. URL Structure
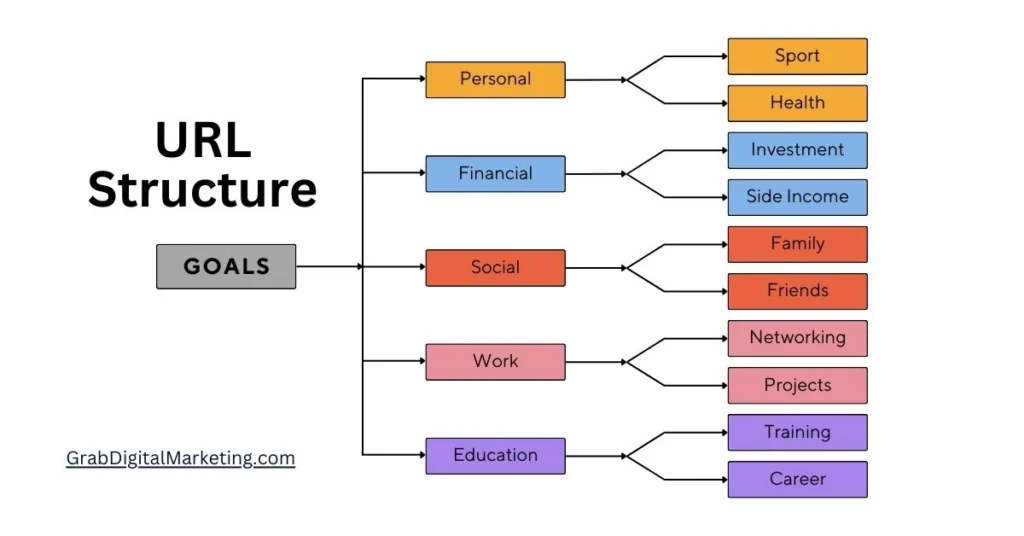
Clean, descriptive URLs improve user experience and search engine understanding. Best practices include:
- Simplicity: Keep URLs short and easy to read.
- Keywords: Include relevant keywords in the URL.
- Hyphens: Use hyphens to separate words, not underscores.
5. Internal Linking

Linking to other pages within your website helps search engines crawl your site and understand its structure. Benefits of internal linking include:
- Improved Navigation: Helps users find related content.
- Link Equity Distribution: Passes link authority to other pages.
- Indexing: Assists search engines in discovering new content.
6. Image Optimization

Optimizing images can improve page load times and provide additional ranking opportunities. Key considerations include:
- Alt Text: Use descriptive alt text to help search engines understand the image content.
- File Size: Compress images to reduce load times without sacrificing quality.
- File Names: Use relevant keywords in image file names.
7. Mobile Friendliness

With the increasing use of mobile devices, ensuring your site is mobile-friendly is crucial. This includes:
- Responsive Design: Use responsive design to ensure your site adapts to different screen sizes.
- Mobile Usability: Ensure buttons, links, and navigation are easily usable on mobile devices.
8. Page Speed
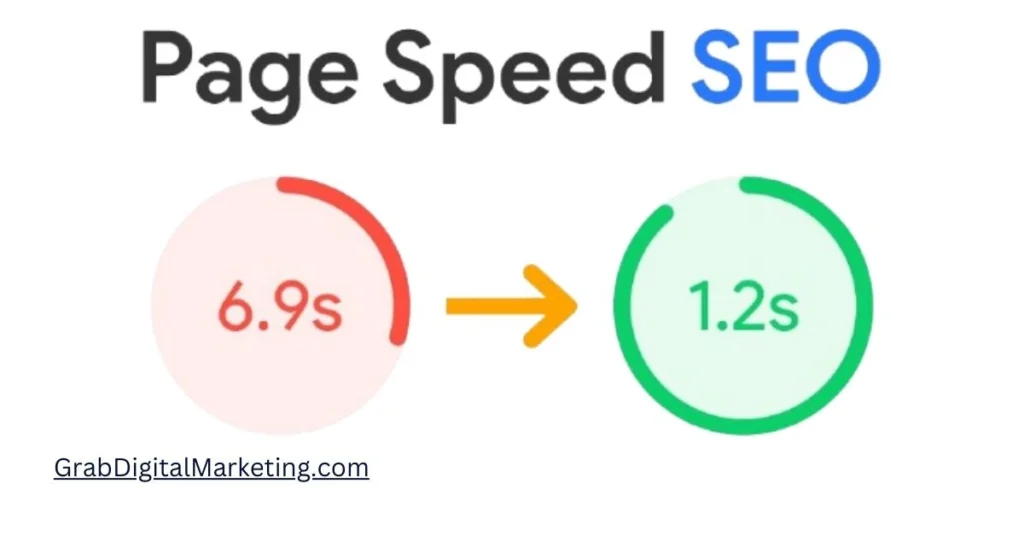
Page speed is a ranking factor and impacts user experience. To optimize page speed:
- Minify Code: Reduce the size of CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files.
- Enable Compression: Use Gzip to compress files.
- Optimize Images: Reduce image sizes without compromising quality.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Store static resources in the browser cache.
9. User Experience (UX)
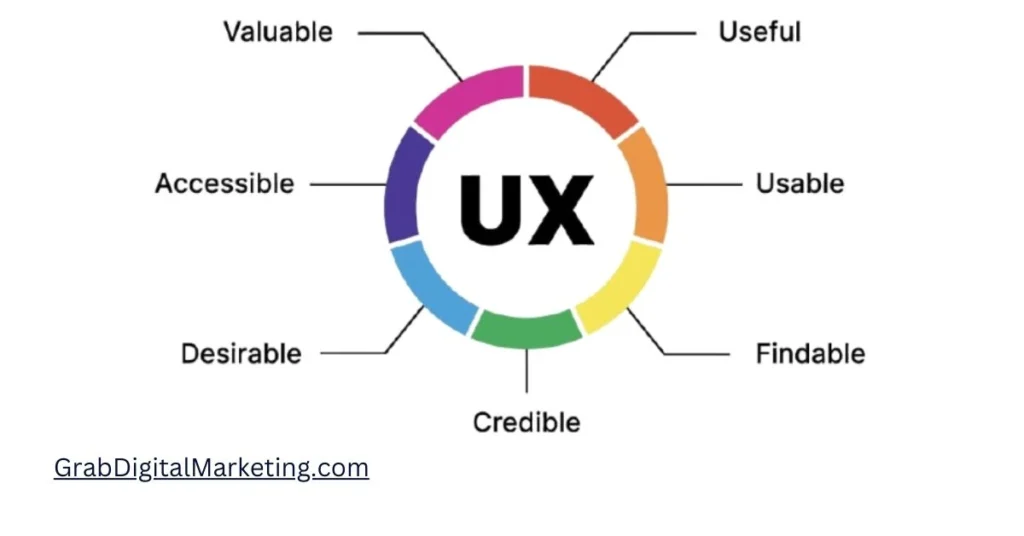
A positive user experience encourages longer visits and lower bounce rates. Key elements include:
- Readability: Use clear, concise language and break content into easily digestible sections.
- Engagement: Include interactive elements like videos, quizzes, and polls.
- Navigation: Ensure intuitive navigation with clear menus and internal links.
10. Social Sharing

Encourage social sharing to increase your content’s visibility. Strategies include:
- Social Buttons: Add social sharing buttons to your pages.
- Click to Tweet: Include “click to tweet” links for sharing key points.
11. Schema Markup

Schema markup helps search engines understand your content and can enhance your search listings with rich snippets. Common types include:
- Article: Use for news articles and blog posts.
- Product: Use product pages to show price, availability, and reviews.
- Review: Use pages with reviews to display star ratings.
12. Security
Ensure your site is secure, as HTTPS is a ranking factor. Steps to enhance security include:
- SSL Certificate: Install an SSL certificate to encrypt data.
- Regular Updates: Keep your CMS, plugins, and themes up to date.
- Secure Login: Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication.
13. Analytics and Monitoring

Regularly monitor and analyze your on-page SEO efforts. Tools include:
- Google Analytics: Track user behavior and identify areas for improvement.
- Google Search Console: Monitor search performance and identify issues.
- SEO Tools: Use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz for in-depth analysis.
14. Content Freshness

Regularly updating your content signals to search engines that your site is current and relevant. Strategies include:
- Content Audits: Regularly review and update old content.
- Add Value: Include new information, insights, or media.
- Repurpose Content: Convert blog posts into videos, infographics, or social media posts.
15. Multilingual SEO

If you target a global audience, consider optimizing your site for multiple languages. Best practices include:
- Hreflang Tags: Use hreflang tags to indicate language and regional targeting.
- Localized Content: Create content specific to each target market.
- By implementing these on-page SEO strategies, you can improve your website’s visibility, user experience, and search engine rankings. Remember, SEO is an ongoing process, and staying updated with the latest trends and algorithm changes is essential for long-term success.
- I hope this comprehensive guide helps you craft an informative blog post on on-page SEO! If you need more details or have specific questions, feel free to ask.




